Hello ,
the JavaScript environment uses the Rhino engine 1.7R4 and it bases on Java. Node.js is another engine. To "simulate" getModule in Node.js you can try this:
// Begin----------------------------------------------------------------
var com = {
vmware : {
// Module com.vmware.basic------------------------------------------
basic : {
createDirectory : function(directory) {
var fs = require('fs');
if (!fs.existsSync(directory)){
console.log("Creating directory : '" + directory + "'");
fs.mkdirSync(directory);
console.log("Directory '" + directory + "' created.");
}
},
getFileName : function(fileName) {
if (fileName != null) {
var index = fileName.lastIndexOf("/");
return fileName.substring(index + 1, fileName.length);
}
return null;
}
},
// Module com.vmware.constants--------------------------------------
constants : {
getDefaultCompanyName : function() {
return "VMware Inc.";
},
getDefaultSSHKeyPairPath : function() {
return "/usr/lib/vco/app-server/conf/vco_key";
}
}
}
}
function getModule(object) {
return Object.create(object);
}
// Main-----------------------------------------------------------------
console.log(
getModule(com.vmware.constants).getDefaultCompanyName()
);
var constants = getModule(com.vmware.constants);
console.log(constants.getDefaultCompanyName());
// End------------------------------------------------------------------
At first I created two modules com.vmware.basic and com.vmware.constants. The function getModule contains only an Object.create command. This is the Node.js equivalent.
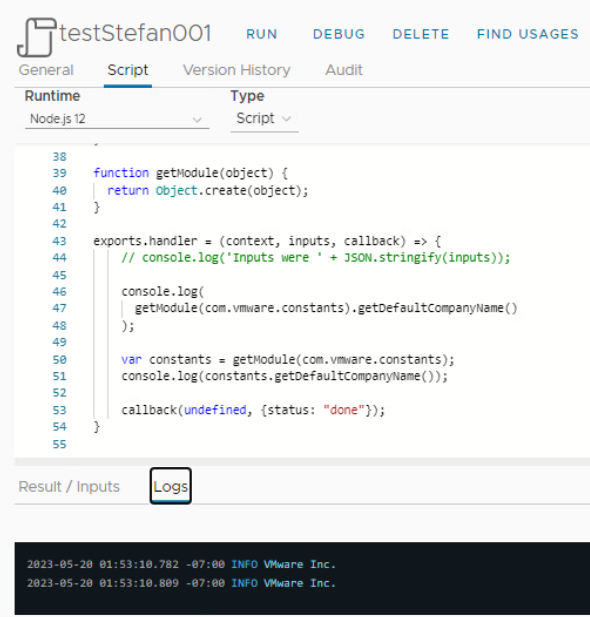
If your question was about using the JavaScript modules with the Node.js runtime, then I suppose for the most part this won't work. This is because the JavaScript engine (Rhino) is based on Java and Node.js is its own JavaScript engine.
Best regards
Stefan