Troubleshooting issues with the Intel® AMT setup and configuration process can be a daunting prospect. This series walks through the troubleshooting methods to pinpoint where problems originate and how to fix them.
Part 6: Real-Time System Manager
Connection Issues
Invalid FQDN
Real-Time Unable To Connect
Authentication Issues
Authentication Methods
Troubleshooting Authentication
IDE Redirect (IDER)
IDER or SOL Disabled
Real-Time System Manager provides a powerful set of functions for IT specialists. In the previous section of this guide I covered the main points for Real-Time Console Infrastructure troubleshooting. As a natural extension of RTCI, Real-Time System Manager troubleshooting will tie directly into what was provided under RTCI. With an emphasis on credentials and connection methods, for all the underlining components (RTCI, Credential Manager, PPA) the main symptoms for issues usually manifest in the Solution trying to use them, whether Task Server or the Real-Time console.
Real-Time System Manager provides a powerful tool for directly connecting to a system agentlessly with functionality available through primarily WMI and Intel AMT. The following sections cover areas of troubleshooting:
- Connection Issues
- Authentication Issues
- IDE Redirect (IDER)
- Network Filtering
Connection Issues
Under the current architecture the FQDN is the primary method for connecting and authenticating to AMT on remote systems. If the FQDN being used by the Real-Time tab does not resolve in DNS, then AMT connectivity and thus functionality will not be available. FQDN connectivity issues are the number one issues we see with RTSM connections to AMT.
Invalid FQDN
To view what FQDN Real-Time System Manager is using, use the 'Hardware Management' node in the RTSM tree. The following screenshot shows what AMT is using:
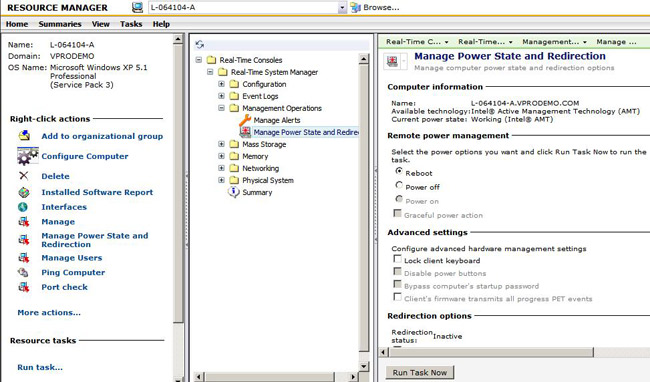
In this example my system is joined to the domain vProDemo and reported as the FQDN, which DNS had no trouble resolving. If this FQDN is not reachable via DNS, we won't be able to connect to the AMT functionality. The primary reason for relying on the FQDN for AMT is if TLS is enabled, the computer's FQDN is required as part of the authentication process.
NOTE: We use several methods, including IP address, for WMI. WMI functionality may show correctly when AMT is absent in this situation.
Use these steps to resolve the FQDN is the issue:
- In the Symantec Management Console, bring up Resource Manager for your vPro enabled system.
- Click the Manage link in the left-hand pane, or from a collection or report right-click on a system and choose Remote Management > Manage.
- Once the tree loads in the middle pane, the right pane will provide a summary of the connection. Under the Supported Protocols section, if all is working you should see "Intel® Active Management Technology (AMT)" with a Status of OK.
- If AMT is missing as an available technology, take note of the name displayed as in the screenshot above.
- Go to Start, Run, type in cmd, and click OK.
- Type in nslookup <name displayed>. In the above example it would read:
- Nslookup L-064104-A.vprodemo.com
- Can DNS resolve this address? If no, we'll need to fix the issue in one of the following ways.
- FIX DNS and/or the Altiris record: If DNS can be fixed, this is the preferred method. The difficulty is finding out why the Altiris Agent reported the incorrect record. Once DNS is fixed, have the Altiris Agent run Basic Inventory. The table location we pull this out of for management in RTSM is Inv_AeX_AC_Location, column: [Fully Qualified Domain Name].
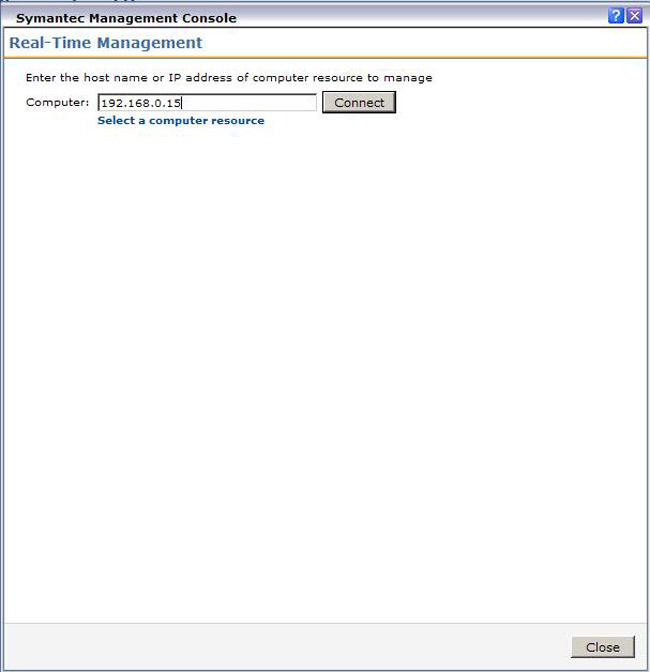
- You can use the Real-Time Management link found under Actions > Remote Management > Real-Time Management. In the resulting window, type in the IP address or FQDN of the system, as shown:
- Update the Server's HOSTS or LMHOSTS files to contain the mapping to the invalid name. For example find the LMHOSTS file, edit it and add a line <IP ADDRESS> <FQDN>, as in this example:
- 10.10.10.1 L-064104-A.vprodemo.com
Real-Time unable to connect
If WMI and AMT functions are unavailable, you'll get a message when you try to launch Real-Time Management indicating that the functionality isn't available. See the following screenshot:
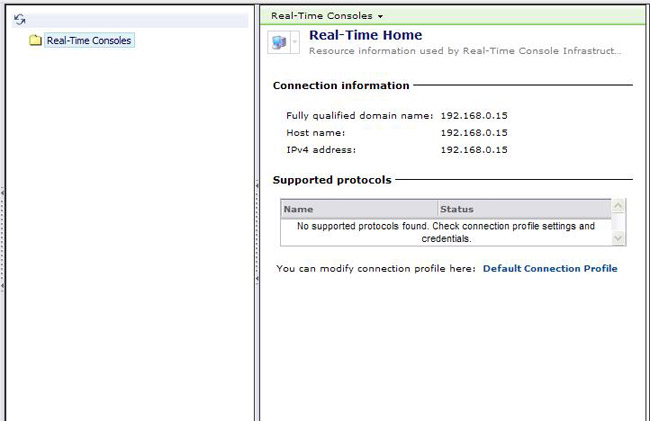
Note: If you use another product such as Dell or HP's plug-ins to this console, you'll simply not have the 'Real-Time System Manager' node underneath Real-Time Consoles.
The number one reason this occurs is due to a firewall being engaged. Firewalls need to allow AMT traffic through. If a firewall is enabled, use the following details to resolve the AMT issue:
- Create an inclusion in the firewall properties.
- Allow the following ports, based off your environment:
- 16992 - For non-TLS encrypted traffic - if you are not using TLS this is the port that will be used for communication
- 16993 - For TLS-enabled, encrypted AMT traffic - If https is required for communication with AMT, this port will be used
- 16994 -AMT setup and configuration uses this port for sending out the 'hello' packet during the configuration process - this will be used if you initiate a reconfigure from RTSM
- Another option is to disable the firewall when you need to manage the system via RTSM.
- Unfortunately WMI has a known issue with the Windows firewall where the dynamic ports WMI uses after initiation will be blocked. It's a bug in WMI that has been addressed in Vista and Windows 7. Previous Operating Systems do not have a resolution at this time.
The other issue we've seen is where the system is simply unavailable for one reason or another. AMT is available if the system is off but still connected to the network, but WMI or if the system is unplugged from power or off the network RTSM obviously cannot function. Verify that the system is available if nothing resolves this issue. Methods include:
- Attempt to connect to the system via Remote Desktop.
- From a command prompt ping the system by Name, IP Address, or FQDN.
- Check Resource Manager to see when the last time the system requested a Client Configuration or sent in Basic Inventory.
Authentication Issues
Another common issue concerns authentication to the system via the Real-Time Management. First, let me discuss the methods RTSM uses to authenticate to a target system.
Authentication Methods
Runtime Profile - The Runtime profile contains the following information:
- All known good credentials used to connect via RTSM to a system
- The Intel SCS AMT password sent to systems when setup and configuration occurs
- Previously successfully used credentials from past RTSM sessions
User-defined Connection Profiles via PPA - Profiles can be created that specifically provide credentials for a myriad of technologies, including the ones supported by RTSM:
- WMI digest or Domain account
- AMT digest or Kerberos-authenticated user
- ASF digest or Domain account
- SNMP community strings
Manually entered credentials - If credentials aren't working according to the status of the protocols, you can edit the Connection Profile in use to supply working credentials, or you can create a new one to select. See the previous section on Pluggable Protocol Architecture on how a Profile is setup.
Troubleshooting Authentication
The following method will help identify and offer ways to work-around or solve issues. These have been compiled through experience when troubleshooting issues with failed authentication via PPA and RTSM.
- In the Symantec Management Console browse under Settings > All Settings > Monitoring and Alerting > Protocol Management > Connection Profiles > and select Manage Connection Profiles.
- What Profile appears when you launch the Real-Time Management console? By default it is the Default Connection Profile.
- For troubleshooting purposes, create a new profile by clicking the blue + on the icon bar.
- By default all protocols will be disabled. Expand the section for AMT (Active Management Technology).
- Click the blue plus next to the first "Select existing credentials" dropdown.
- Create a Credential specific for AMT, that you know works against the target system. Once completed it will show as the selection under the dropdown.
- For the rest of the options, check and supply details as needed.
- Change the protocol to ON (it will show as a green bar instead of red).
- Expand the section for ICMP. This will be used to initially engage the system for detection of other supported protocols.
- Change the Timeout to 2000 and Retry count to 3. This will avoid timeouts causing the inability to connect to the other protocols.
- Change ICMP to ON.
- If so desired, also supply WMI credentials to unlock those functions. Follow the same basic steps as the AMT credential setup. See this screenshot for an example of the newly configured profile:

- Give the Connection profile a name and then save it by clicking OK.
- Back at the Real-Time Management console, change the Profile by clicking the hyperlink next to the label: You can modify connection profile here:.
- Once you've selected the new Profile, RTSM will try to reconnect using the new credentials supplied in the new connection profile.
- If it still fails, check the system name or IP address listed next to the Resource Manager banner. You should also look under Connection information as sometimes we resolve to a different machine than the original intended.
IDE Redirect (IDER)
IDE Redirect allows a system to be remotely booted to a file, drive, or virtual disc. There are a number of potential issues to be aware of when working with IDER in a vPro environment. The below item includes a specific issue and the resolution.
IDER or SOL Disabled
In some instances Intel vPro systems are arriving from the OEM with IDER and SOL disabled in the BIOS. When disabled, neither of these functions work from any management engine, including RTSM. Correcting this oversight is not easy, especially if the OEMs do not offer a solution by a firmware or BIOS update. Use the following method to resolve the issue:
- Go to the Support site for the OEM for the systems.
- Browse to the drivers and downloads section for the exact model (note that sometimes the model will differ based on possessing or not possessing vPro technology).
- Check the firmware updates for a new BIOS.
- Check the documentation for any new BIOS versions that include vPro to see if they've corrected this.
- Contact your OEM if they have not and request a status!
- The only other recourse is to develop an update yourself that can be deployed via a Windows Application file. When completed this can be delivered with Software Management Solution or similar deployment engine.
Return to Part 1/Index
Read Part 7: Task Server